Training and Finetuning Reranker Models with Sentence Transformers v4 | 使用Sentence Transformers v4训练和微调重排模型
学习如何使用Sentence Transformers v4训练和微调重排模型以提高检索性能。Learn how to train and finetune reranker models with Sentence Transformers v4 to improve retrieval performance.
Training and Finetuning Reranker Models with Sentence Transformers v4 | 使用Sentence Transformers v4训练和微调重排模型
Sentence Transformers is a Python library for using and training embedding and reranker models for a wide range of applications, such as retrieval augmented generation, semantic search, semantic textual similarity, paraphrase mining, and more. Its v4.0 update introduces a new training approach for rerankers, also known as cross-encoder models, similar to what the v3.0 update introduced for embedding models. In this blogpost, I'll show you how to use it to finetune a reranker model that beats all existing options on exactly your data. This method can also train extremely strong new reranker models from scratch.
Sentence Transformers是一个Python库,用于使用和训练嵌入和重排模型,适用于各种应用,如检索增强生成、语义搜索、语义文本相似性、同义句挖掘等。其v4.0更新为重排器引入了新的训练方法,也称为交叉编码器模型,类似于v3.0更新为嵌入模型引入的方法。在这篇博客文章中,我将向您展示如何使用它来微调一个在您的数据上击败所有现有选项的重排模型。这种方法也可以从头开始训练极其强大的新重排模型。
Finetuning reranker models involves several components: datasets, loss functions, training arguments, evaluators, and the trainer class itself. I'll have a look at each of these components, accompanied by practical examples of how they can be used for finetuning strong reranker models.
微调重排模型涉及几个组件:数据集、损失函数、训练参数、评估器和训练器类本身。我将查看每个组件,并附上如何用于微调强大重排模型的实际示例。
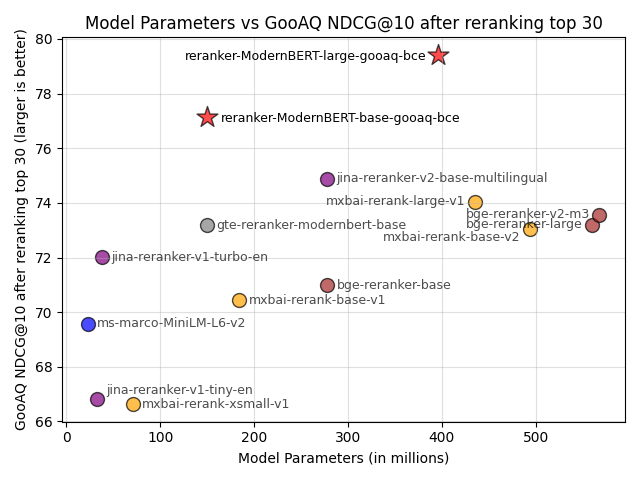
Lastly, in the Evaluation section, I'll show you that my small finetuned tomaarsen/reranker-ModernBERT-base-gooaq-bce reranker model that I trained alongside this blogpost easily outperforms the 13 most commonly used public reranker models on my evaluation dataset. It even beats models that are 4x bigger.
最后,在评估部分,我将向您展示我微调的小型tomaarsen/reranker-ModernBERT-base-gooaq-bce重排模型(我在撰写这篇博客文章时训练的)在我的评估数据集上轻松击败了13个最常用的公共重排模型。它甚至击败了大4倍的模型。
Repeating the recipe with a bigger base model results in tomaarsen/reranker-ModernBERT-large-gooaq-bce, a reranker model that blows all existing general-purpose reranker models out of the water on my data.
使用更大的基础模型重复这个方法,得到了tomaarsen/reranker-ModernBERT-large-gooaq-bce,这是一个在我的数据上击败所有现有通用重排模型的重排模型。
If you're interested in finetuning embedding models instead, then consider reading through my prior Training and Finetuning Embedding Models with Sentence Transformers v3 blogpost as well.
如果您对微调嵌入模型更感兴趣,请考虑阅读我之前的使用Sentence Transformers v3训练和微调嵌入模型博客文章。
What are Reranker models? | 什么是重排模型?
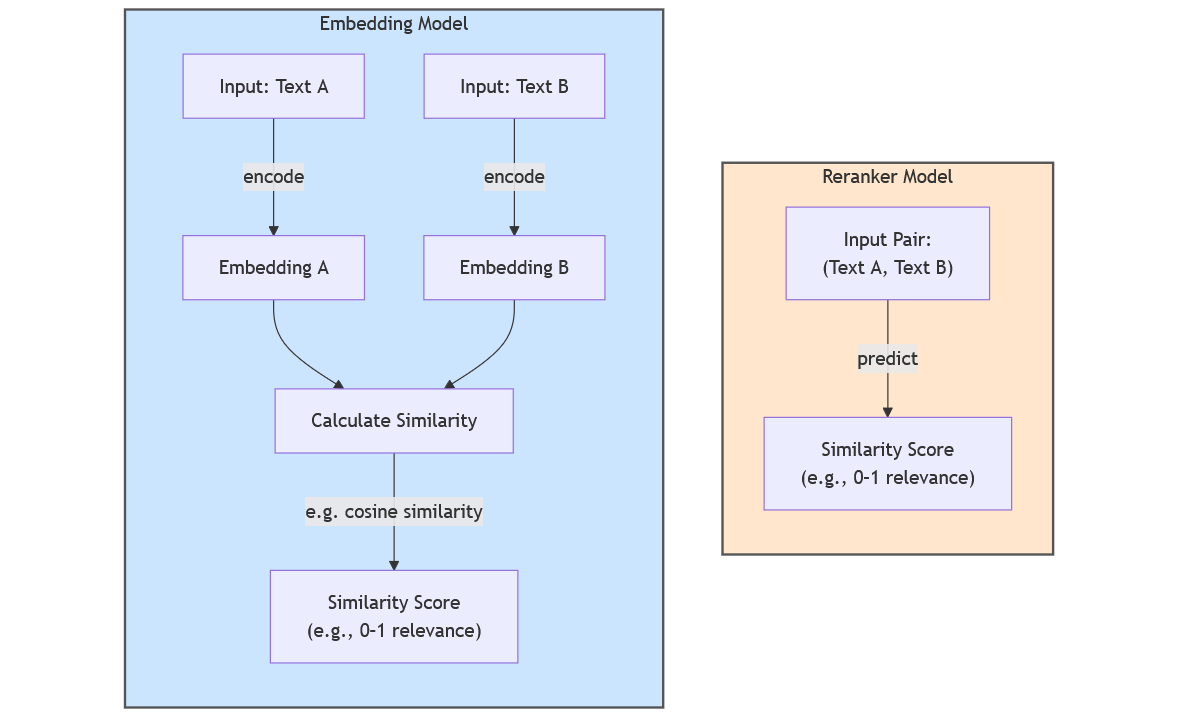
Reranker models, often implemented using Cross Encoder architectures, are designed to evaluate the relevance between pairs of texts (e.g., a query and a document, or two sentences). Unlike Sentence Transformers (a.k.a. bi-encoders, embedding models), which independently embed each text into vectors and compute similarity via a distance metric, Cross Encoder process the paired texts together through a shared neural network, resulting in one output score. By letting the two texts attend to each other, Cross Encoder models can outperform embedding models.
重排模型通常使用交叉编码器架构实现,旨在评估文本对(例如查询和文档,或两个句子)之间的相关性。与Sentence Transformers(也称为双编码器、嵌入模型)不同,后者将每个文本独立嵌入到向量中并通过距离度量计算相似性,交叉编码器通过共享神经网络一起处理成对的文本,产生一个输出分数。通过让两个文本相互关注,交叉编码器模型可以超越嵌入模型。
However, this strength comes with a trade-off: Cross Encoder models are slower as they process every possible pair of texts (e.g., 10 queries with 500 candidate documents requires 5,000 computations instead of 510 for embedding models). This makes them less efficient for large-scale initial retrieval but ideal for reranking: refining the top-k results first identified by faster Sentence Transformer models. The strongest search systems commonly use this 2-stage "retrieve and rerank" approach.
然而,这种优势伴随着权衡:交叉编码器模型较慢,因为它们处理每一对可能的文本(例如,10个查询与500个候选文档需要5,000次计算,而嵌入模型只需要510次)。这使得它们在大规模初始检索中效率较低,但对于重排来说是理想的:优化由更快的Sentence Transformer模型首先识别的top-k结果。最强大的搜索系统通常使用这种两阶段的"检索和重排"方法。
Throughout this blogpost, I'll use "reranker model" and "Cross Encoder model" interchangeably.
在整篇博客文章中,我将交替使用"重排模型"和"交叉编码器模型"。
Why Finetune? | 为什么要微调?
Reranker models are often tasked with a challenging problem:
重排模型通常面临一个具有挑战性的问题:
Which of these k highly-related documents answers the query the best?
这些k个高度相关的文档中,哪个最好地回答了查询?
General-purpose reranker models are trained to perform adequately on this exact question in a wide range of domains and topics, preventing them from reaching their maximum potential in your specific domain. Through finetuning, the model can learn to focus exclusively on the domain and/or language that matters to you.
通用重排模型被训练为在各种领域和主题中对这个确切问题表现良好,这阻止了它们在您的特定领域中发挥最大潜力。通过微调,模型可以学会专注于对您重要的领域和/或语言。
In the Evaluation section end of this blogpost, I'll show that training a model on your domain can outperform any general-purpose reranker model, even if those baselines are much bigger. Don't underestimate the power of finetuning on your domain!
在本文末尾的评估部分,我将展示在您的领域上训练模型可以超越任何通用重排模型,即使这些基线模型大得多。不要低估在您的领域上微调的力量!
Training Components | 训练组件
Training reranker models involves the following components:
训练重排模型涉及以下组件:
-
Dataset: The data used for training and/or evaluation.
数据集: 用于训练和/或评估的数据。
-
Loss Function: A function that measures the model's performance and guides the optimization process.
损失函数: 衡量模型性能并指导优化过程的函数。
-
Training Arguments (optional): Parameters that impact training performance, tracking, and debugging.
训练参数(可选): 影响训练性能、跟踪和调试的参数。
-
Evaluator (optional): A class for evaluating the model before, during, or after training.
评估器(可选): 在训练前、训练中或训练后评估模型的类。
-
Trainer: Brings together all training components.
训练器: 整合所有训练组件。
Let's take a closer look at each component.
让我们更仔细地看看每个组件。
Dataset | 数据集
The CrossEncoderTrainer uses datasets.Dataset or datasets.DatasetDict instances for training and evaluation. You can load data from the Hugging Face Datasets Hub or use your local data in whatever format you prefer (e.g. CSV, JSON, Parquet, Arrow, or SQL).
CrossEncoderTrainer使用datasets.Dataset或datasets.DatasetDict实例进行训练和评估。您可以从Hugging Face数据集中心加载数据,或使用您喜欢的任何格式的本地数据(例如CSV、JSON、Parquet、Arrow或SQL)。
Note: Lots of public datasets that work out of the box with Sentence Transformers have been tagged with sentence-transformers on the Hugging Face Hub, so you can easily find them on https://huggingface.co/datasets?other=sentence-transformers. Consider browsing through these to find ready-to-go datasets that might be useful for your tasks, domains, or languages.
注意: 许多与Sentence Transformers开箱即用的公共数据集在Hugging Face Hub上被标记为sentence-transformers,因此您可以轻松在https://huggingface.co/datasets?other=sentence-transformers上找到它们。考虑浏览这些数据集,找到可能对您的任务、领域或语言有用的现成数据集。
Data on the Hugging Face Hub | Hugging Face Hub上的数据
You can use the load_dataset function to load data from datasets in the Hugging Face Hub
您可以使用load_dataset函数从Hugging Face Hub中的数据集加载数据
from datasets import load_dataset
train_dataset = load_dataset("sentence-transformers/natural-questions", split="train")Local Data (CSV, JSON, Parquet, Arrow, SQL) | 本地数据(CSV、JSON、Parquet、Arrow、SQL)
You can load local data using the same load_dataset function:
您可以使用相同的load_dataset函数加载本地数据:
from datasets import load_dataset
# Load from CSV
train_dataset = load_dataset("csv", data_files="train.csv", split="train")
# Load from JSON
train_dataset = load_dataset("json", data_files="train.json", split="train")
# Load from Parquet
train_dataset = load_dataset("parquet", data_files="train.parquet", split="train")Loss Function | 损失函数
The loss function is crucial for training reranker models. Sentence Transformers v4 introduces several new loss functions specifically designed for reranker training:
损失函数对训练重排模型至关重要。Sentence Transformers v4引入了几种专门为重排训练设计的新损失函数:
-
BCE (Binary Cross Entropy): Good for pairwise ranking tasks
-
BCE(二元交叉熵): 适用于成对排名任务
-
Contrastive Loss: Useful for learning to distinguish between relevant and irrelevant pairs
-
对比损失: 有助于学习区分相关和不相关的对
-
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss: Effective for learning to rank multiple negative examples against a positive one
-
MultipleNegativesRankingLoss: 有效地学习将多个负例与一个正例进行排名
Here's an example of using BCE loss:
以下是使用BCE损失的示例:
from sentence_transformers.losses import BCE
loss = BCE(
sentence_embedding_dimension=model.get_sentence_embedding_dimension(),
num_labels=1
)Training Arguments | 训练参数
Training arguments control various aspects of the training process:
训练参数控制训练过程的各个方面:
from sentence_transformers.training_args import SentenceTransformerTrainingArguments
args = SentenceTransformerTrainingArguments(
output_dir="reranker-model",
num_train_epochs=3,
per_device_train_batch_size=8,
per_device_eval_batch_size=8,
warmup_ratio=0.1,
learning_rate=2e-5,
logging_steps=100,
save_steps=500,
evaluation_strategy="steps",
eval_steps=500,
save_total_limit=2,
dataloader_pin_memory=False,
)Evaluator | 评估器
Evaluators help track model performance during training:
评估器帮助跟踪训练期间的模型性能:
from sentence_transformers.evaluation import CrossEncoderRerankingEvaluator
evaluator = CrossEncoderRerankingEvaluator(
name="gooaq-mined-negatives",
queries=eval_queries,
relevant_docs=eval_relevant_docs,
corpus=eval_corpus,
mrr_at_k=[10, 100],
ndcg_at_k=[10, 100],
accuracy_at_k=[1, 3, 5, 10, 100],
)Trainer | 训练器
The trainer brings everything together:
训练器将所有内容整合在一起:
from sentence_transformers import CrossEncoderTrainer
trainer = CrossEncoderTrainer(
model=model,
args=args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
loss=loss,
evaluator=evaluator,
)Training Tips | 训练技巧
Here are some key tips for training effective reranker models:
以下是训练有效重排模型的一些关键技巧:
-
Data Quality: Ensure your training data is high-quality and representative of your target domain.
数据质量: 确保您的训练数据高质量且能代表您的目标领域。
-
Negative Sampling: Use hard negatives when possible to improve model performance.
负采样: 尽可能使用困难负例来提高模型性能。
-
Model Size: Larger models generally perform better but require more computational resources.
模型大小: 较大的模型通常表现更好,但需要更多计算资源。
-
Learning Rate: Start with a lower learning rate (e.g., 2e-5) and adjust based on performance.
学习率: 从较低的学习率开始(例如2e-5),并根据性能进行调整。
-
Evaluation: Regularly evaluate your model on a held-out dataset to track progress.
评估: 定期在保留数据集上评估您的模型以跟踪进度。
Evaluation | 评估
As mentioned earlier, my finetuned reranker model significantly outperforms existing models on my evaluation dataset. Here are the key results:
如前所述,我微调的重排模型在我的评估数据集上显著优于现有模型。以下是关键结果:

The results show that:
结果显示:
-
Domain-specific training significantly improves performance over general-purpose models.
领域特定训练显著提高了性能,优于通用模型。
-
Smaller, finetuned models can outperform much larger general-purpose models.
较小的微调模型可以超越大得多的通用模型。
-
Sentence Transformers v4 provides an effective framework for training state-of-the-art reranker models.
Sentence Transformers v4为训练最先进的重排模型提供了有效的框架。
Additional Resources | 附加资源
Conclusion | 结论
Training and finetuning reranker models with Sentence Transformers v4 provides a powerful approach to improving retrieval performance in specialized domains. By leveraging the new training components and techniques, you can develop models that significantly outperform general-purpose alternatives, even when those alternatives are much larger.
使用Sentence Transformers v4训练和微调重排模型为提高特定领域的检索性能提供了强大的方法。通过利用新的训练组件和技术,您可以开发出显著优于通用替代方案的模型,即使这些替代方案大得多。
The key takeaways are:
关键要点是:
-
Domain-specific finetuning is crucial for optimal performance in specialized applications.
领域特定微调对于专业应用中的最佳性能至关重要。
-
Cross-encoder models can provide superior accuracy compared to bi-encoder approaches.
交叉编码器模型可以提供比双编码器方法更优越的准确性。
-
Sentence Transformers v4 offers a comprehensive framework for training state-of-the-art reranker models.
Sentence Transformers v4为训练最先进的重排模型提供了全面的框架。
By following the approach outlined in this blogpost, you can train your own high-performing reranker models tailored to your specific use cases and domains.
通过遵循本博客文章中概述的方法,您可以训练针对特定用例和领域的高性能重排模型。