[文本分块]RAG 中分块策略的五个级别
本文来自格雷格视频,视频已经放在文章末尾
[文本分块]RAG 中分块策略的五个级别
Introduction 介绍
Breaking down your large data files into more manageable segments is one of the most crucial steps for enhancing the efficiency of LLM applications. The goal is to provide the LLM with precisely the information needed for the specific task, and nothing more.
将大型数据文件分解为更易于管理的部分是提高LLM应用程序效率的最关键步骤之一。目标是为 LLM 提供特定任务所需的准确信息,仅此而已。
"What should be the right chunking strategy in my solution" is one of the initial and fundamental decision a LLM practitioner must make while building advance RAG solution.
"我的解决方案中正确的分块策略应该是什么"是 LLM 从业者在构建高级 RAG 解决方案时必须做出的初始基本决策之一。
In his video, Greg Kamradt provides overview of different chunking strategies. These strategies can be leveraged as starting points to develop RAG based LLM application. They have been classified into five levels based on the complexity and effectiveness.
Greg Kamradt 在他的视频中概述了不同的分块策略。这些策略可以用作开发基于 RAG 的LLM 应用程序的起点。根据复杂性和有效性,它们被分为五个级别。
Your goal is not to chunk for chunking sake, our goal is to get our data in a format where it can be retrieved for value later.
您的目标不是为了分块而分块,我们的目标是以一种格式获取数据,以便以后可以检索数据以获取价值。
Level 1 : Fixed Size Chunking
第 1 级:固定大小分块
This is the most crude and simplest method of segmenting the text. It breaks down the text into chunks of a specified number of characters, regardless of their content or structure.
这是最粗暴、最简单的文本切分方法。它将文本分解为指定数量字符的块,无论其内容或结构如何。
Langchain and llamaindex framework offer CharacterTextSplitter and SentenceSplitter (default to spliting on sentences) classes for this chunking technique. A few concepts to remember -
Langchain 和 llamaindex 框架为这种分块技术提供了 CharacterTextSplitter 和 SentenceSplitter(默认在句子上分割)类。需要记住的几个概念 -
- How the text is split: by single character
文本如何分割:按单个字符 - How the chunk size is measured: by number of characters
如何测量块大小:按字符数 - chunk_size: the number of characters in the chunks
chunk_size:块中的字符数 - chunk_overlap: the number of characters that are being overlap in sequential chunks. keep duplicate data across chunks
chunk_overlap:连续块中重叠的字符数。跨块保留重复数据 - separator: character(s) on which the text would be split on (default " ")
分隔符:文本将被分割的字符(默认" ")
Level 2: Recursive Chunking
第 2 级:递归分块
While Fixed size chunking is easier to implement, it doesn't consider the structure of text. Recursive chunking offers an alternative.
虽然固定大小分块更容易实现,但它没有考虑文本的结构。递归分块提供了一种替代方案。
In this method, we divide the text into smaller chunk in a hierarchical and iterative manner using a set of separators. If the initial attempt at splitting the text doesn't produce chunks of the desired size, the method recursively calls itself on the resulting chunks with a different separator until the desired chunk size is achieved.
在这种方法中,我们使用一组分隔符以分层和迭代的方式将文本划分为更小的块。如果分割文本的初始尝试没有生成所需大小的块,则该方法会使用不同的分隔符在生成的块上递归调用自身,直到达到所需的块大小。
Langchain framework offers RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter class, which splits text using default separators ("\n\n", "\n", " "," ")
Langchain框架提供了RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter类,它使用默认分隔符("\n\n","\n"," "," ")分割文本
Level 3 : Document Based Chunking
第 3 级:基于文档的分块
In this chunking method, we split a document based on its inherent structure. This approach considers the flow and structure of content but may not be as effective documents lacking clear structure.
在这种分块方法中,我们根据文档的固有结构来分割文档。这种方法考虑了内容的流程和结构,但可能不是缺乏清晰结构的有效文档。
- Document with Markdown: Langchain provides MarkdownTextSplitter class to split document that consist markdown as way of separator.
带有 Markdown 的文档:Langchain 提供了 MarkdownTextSplitter 类来分割包含 Markdown 的文档作为分隔符。 - Document with Python/JS: Langchain provides PythonCodeTextSplitter to split the python program based on class, function etc. and We can provide language into from_language method of RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter class.
Python/JS 文档:Langchain 提供了 PythonCodeTextSplitter 来根据类、函数等拆分 python 程序,我们可以将语言提供给 RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter 类的 from_language 方法。 - Document with tables: When dealing with tables, splitting based on levels 1 and 2 might lose the tabular relationship between rows and columns. To preserve this relationship, format the table content in a way that the language model can understand (e.g., using
<table>tags in HTML, CSV format separated by ';', etc.). During semantic search, matching on embeddings directly from the table can be challenging. Developers often summarize the table after extraction, generate an embedding of that summary, and use it for matching.
带表格的文档:处理表格时,基于级别 1 和级别 2 的拆分可能会丢失行和列之间的表格关系。要保留这种关系,请以语言模型可以理解的方式格式化表内容(例如,在 HTML、CSV 格式中使用<table>标记,并用";"分隔等)。在语义搜索过程中,直接从表中匹配嵌入可能具有挑战性。开发人员通常在提取后对表进行汇总,生成该汇总的嵌入,并将其用于匹配。 - Document with images (Multi- Modal): Embeddings for images and text could be contents different (Though CLIP model support this). The ideal tactic is to use multi-modal model (like GPT-4 vision) to generate summaries of the images and store embeddings of it. Unstructured.io provides partition_pdf method to extract images from pdf document.
带有图像的文档(多模态):图像和文本的嵌入内容可能不同(尽管 CLIP 模型支持这一点)。理想的策略是使用多模态模型(如 GPT-4 视觉)来生成图像摘要并存储其嵌入。 Unstructed.io 提供了partition_pdf 方法来从pdf 文档中提取图像。
Level 4: Semantic Chunking
**第 4 级:语义分块
All above three levels deals with content and structure of documents and necessitate maintaining constant value of chunk size. This chunking method aims to extract semantic meaning from embeddings and then assess the semantic relationship between these chunks. The core idea is to keep together chunks that are semantic similar.
所有上述三个级别都涉及文档的内容和结构,并且需要保持块大小的恒定值。这种分块方法旨在从嵌入中提取语义,然后评估这些块之间的语义关系。核心思想是将语义相似的块放在一起.
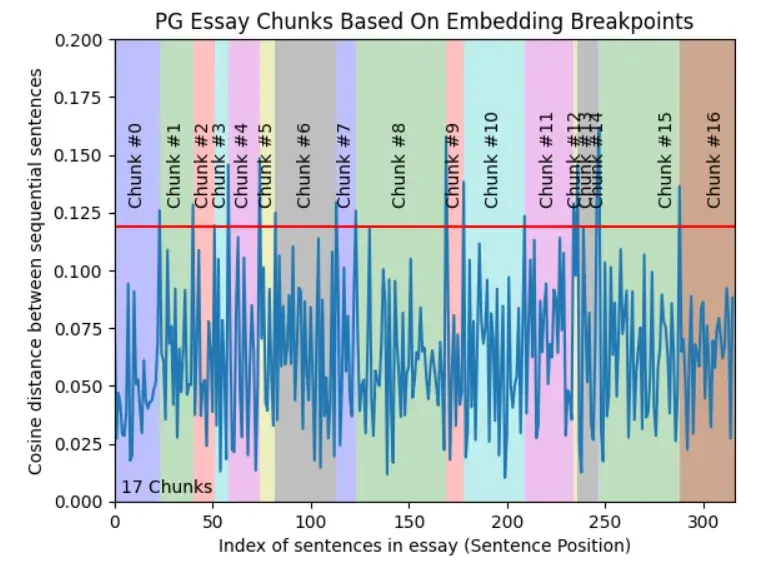
Llamindex has SemanticSplitterNodeParse class that allows to split the document into chunks using contextual relationship between chunks. This adaptively picks the breakpoint in-between sentences using embedding similarity.
Llamindex 具有 SemanticSplitterNodeParse 类,允许使用块之间的上下文关系将文档拆分为块。这使用嵌入相似性自适应地选择句子之间的断点。
few concepts to know 几个需要了解的概念
- buffer_size: configurable parameter that decides the initial window for chunks
buffer_size:可配置参数,决定块的初始窗口 - breakpoint_percentile_threshold: another configurable parameter. The threshold value to decide where to split the chunk
Breakpoint_percentile_threshold:另一个可配置参数。决定在何处分割块的阈值 - embed_mode: the embedding model used.
embed_mode:使用的嵌入模型。
Level 5: Agentic Chunking
第五级:主体分块
This chunking strategy explore the possibility to use LLM to determine how much and what text should be included in a chunk based on the context.
此分块策略探索了使用 LLM 来根据上下文确定块中应包含多少文本和哪些文本的可能性。
To generate initial chunks, it uses concept of Propositions based on paper that extracts stand alone statements from a raw piece of text. Langchain provides propositional-retrieval template to implement this.
为了生成初始块,它使用基于纸张的命题概念,从原始文本中提取独立的陈述。 Langchain 提供了命题检索模板来实现这一点。
After generating propositions, these are being feed to LLM-based agent. This agent determine whether a proposition should be included in an existing chunk or if a new chunk should be created.
生成提议后,这些提议将被提供给基于 LLM 的代理。该代理确定是否应将命题包含在现有块中或是否应创建新块。

Conclusion 结论
In this article, we explored different chunking strategies and methods to implement them in Langchain and Llamaindex framework.
在本文中,我们探索了不同的分块策略以及在 Langchain 和 Llamaindex 框架中实现它们的方法。
To find the code from Greg: https://github.com/FullStackRetrieval-com/RetrievalTutorials/blob/main/tutorials/LevelsOfTextSplitting/5_Levels_Of_Text_Splitting.ipynb
要查找 Greg 的代码:https://github.com/FullStackRetrieval-com/RetrievalTutorials/blob/main/tutorials/LevelsOfTextSplitting/5_Levels_Of_Text_Splitting.ipynb
原视频,非常值得一看
生产就绪的 RAG 应用程序的 12 种调优策略指南
A comprehensive guide on tuning strategies for production-ready RAG applications, covering both ingestion and inferencing stages
[HyDE] 使用假设性文档嵌入(HyDE)改进信息检索和 RAG
了解如何使用假设性文档嵌入(HyDE)改进信息检索和 RAG 系统。Learn how to use Hypothetical Document Embeddings (HyDE) to improve information retrieval and RAG systems.